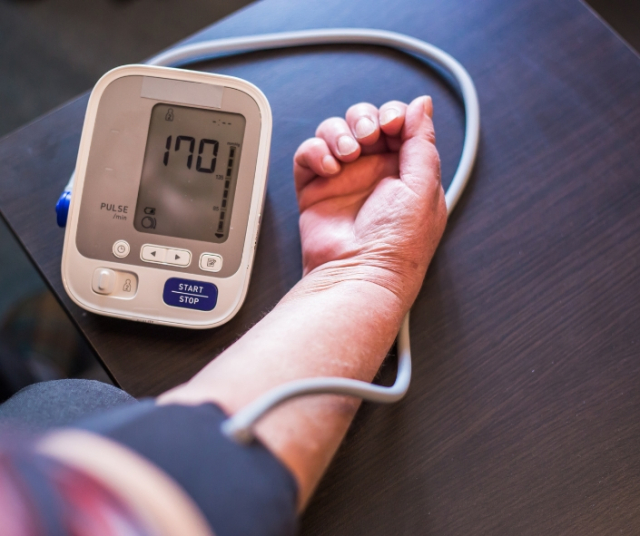
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent and often silent medical condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by the excessive force that blood exerts on the walls of the arteries, which can have serious consequences for cardiovascular health. In this article, we will explore what hypertension is, why it occurs, and the implications it has on human health.
Understanding hypertension.
Blood pressure refers to the force that blood exerts against the walls of the arteries as it is pumped by the heart and circulates through the body. It is measured by two numbers: systolic blood pressure, which is the pressure when the heart beats, and diastolic blood pressure, which is the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats. Blood pressure is expressed in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Under normal conditions, blood pressure is maintained at levels that allow adequate blood flow to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues. However, when these levels constantly increase and are above normal ranges, hypertension is diagnosed.
Risk factors and causes of hypertension.
Hypertension can be the result of a variety of factors, and its cause often cannot be attributed to a single element. Among the most common risk factors are:
Age and genetics:
The likelihood of developing hypertension tends to increase with age. Additionally, genetic predisposition may play a significant role; A person is more likely to have hypertension if they have a family history of the disease.
Lifestyle:
Unhealthy habits, such as a high-sodium diet, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking, can contribute to the development of hypertension. These factors can trigger weight gain and the buildup of plaques in the arteries, contributing to arterial stiffness.
Underlying diseases:
Medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease and sleep apnea can increase the risk of hypertension. These conditions affect fluid balance and blood vessel function.
Stress:
Chronic stress situations can trigger hormonal responses that affect blood pressure. Although stress itself does not directly cause hypertension, it can contribute to the development of poor lifestyle habits that do.
Consequences of hypertension.
Hypertension can have serious and life-threatening consequences if not properly controlled. Some of the associated complications include:
Cardiovascular Disease:
Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke. Constant stress on the arteries can lead to their hardening and narrowing, increasing the chances of cardiovascular events.
Kidney damage:
High blood pressure can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, affecting their ability to properly filter waste from the body and regulate blood pressure.
Visual problems:
Hypertension can affect the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and even vision loss.
Brain problems:
The risk of stroke is significantly increased with hypertension, since high blood pressure can damage the arteries in the brain.
Diagnosis and treatment of hypertension.
Early detection and effective management of hypertension are essential to prevent long-term complications. Doctors use a sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure and establish a diagnosis. Readings consistently higher than 130/80 mm Hg are considered hypertension.
Common treatments include:
Changes in lifestyle:
Adopting a healthy low-sodium diet, increasing physical activity, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking are key lifestyle changes to control hypertension.
Medicines:
In some cases, antihypertensive medications may be prescribed to help control blood pressure. These may include diuretics, beta blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), and others.
Regular monitoring:
Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as necessary.
Prevention of hypertension.
Preventing hypertension involves addressing modifiable risk factors. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy body weight, limiting sodium intake, and getting regular medical checkups are key steps in preventing the development of hypertension.
Reducing alcohol consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to increased blood pressure. Moderation is key, and it is recommended to limit alcohol consumption to moderate amounts based on health guidelines. For men, this generally means no more than two drinks a day, and for women, no more than one.
Give up smoking:
Smoking is a major risk factor for hypertension and a host of health problems. The chemicals present in tobacco can damage arteries and increase blood pressure. Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions someone can make to improve their cardiovascular health.
Effective stress management:
Although stress alone does not cause hypertension, it can trigger physiological responses that affect blood pressure. Effective stress management through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or practicing relaxing activities can be beneficial in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Limit caffeine:
The role of caffeine on blood pressure is debated, but some studies suggest that it may have a temporary effect on raising blood pressure. While the exact relationship is unclear, limiting caffeine consumption may be a prudent choice, especially if you are sensitive to its effects.
Hypertension is a serious medical condition that can have serious consequences if not managed properly. Understanding its causes, risk factors and complications is essential to effectively address this disease and promote long-term cardiovascular health. Adopting lifestyle changes and a proactive approach to healthcare are critical in combating hypertension and promoting healthy living.